Taxonomy
Taxonomy etymology [Gk- Taxis = “arrangement”; Nomos = “Law”]
The branch of biology deals with identification, classification and nomenclature of organisms is called Taxonomy.
Taxonomy word is coined by A. P. De Candolle. Theories Element ire De La Botanique (Theory of elementary biology) is written by De Candolle.
Carolus Linnaeus is known as the father of taxonomy.
Identification
Comparing similarities and differences of organisms.
Classification
The arrangement of organisms in the different group according to similarities and differences
Nomenclature
Providing unique and universal names to organisms like Homo sapiens for Human.
Types of Taxonomy
Morphotaxonomy – Classifications of organisms according to their morphology.
Cytotaxonomy – Classifications of organisms according to their cellular structure. Cytochrome C is the main basis of classification.
Chemotaxonomy – Classifications of organisms according to biochemicals presents in the cell. Proteins present in cells are the main basis of classification.
Karyotaxonomy – Classifications of organisms according to nucleus and chromosome present in the cell.
Numerical-taxonomy – Classifications of organisms according to numbers provided by their characters. It is also known as Adansonian taxonomy.
Levels of Taxonomy
Alpha Taxonomy
It is also known as classical taxonomy which concerned with finding, describing, and naming of organisms according to their morphology and evolution.
Beta Taxonomy
This level of taxonomy includes classifying organisms in different groups.
Gamma Taxonomy
It concerned with the evolutionary study of organisms. It is a broad level of taxonomy therefore also known as encyclopedia taxonomy.
Systematics
[Systema = “system”]
Study of the morphology of organisms and their relationships is called Systematics. Systematics word is given by Linnaeus
Taxonomy and systematic are conjointly known as systematic biology.
Neosystematics
[Neo = “New”; Systema = “system”]
Neosystematics is the science which deals with morphological, anatomical, cytological, embryological, genetically and evolutionary studies of organisms and their relationships. The concept of new systematic is given by J. Huxley.
Neosystematics is also known as biosystematics.
History of Classifications
384-322 BC Aristotle firstly classified the organisms in two group Plants and Animals. The plants were further divided into three groups which are Shrubs, Herbs and Trees and Animals were further divided into two groups which are Aniama (absence of RBC) and Eniama (Presence of RBC)
In the 18th century, Carolus Linnaeus classified organisms in two kingdoms Plantae and Animalia.
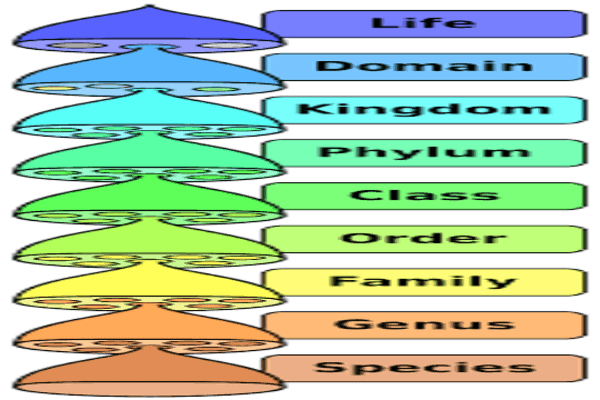
Taxon of Classification
A taxon is a unit of classification. It indicates a group of organisms. Following taxon are used in classifications –
1. Species – It is the smallest taxon. It is a group of similar organisms like Leo for lion, Pardus for Leopard and Tigris for tiger.
Lion – Panthera leo,
Leopard – Panthera pardus,
Tiger – Panthera tigris.
2. Genus– It is a group of similar species like Panthera for Lion, Leopard, Tiger and Felis for cats.
3. Family– It is a group of similar genus like Panthera and Felis genus has a family Felidae.
4. Order – It is a group of similar families. like Felidae (cat family), Canidae (dog family) are put together in an order Carnivora.
5. Class – Similar orders put together in class. Example Carnivora (tiger, cat, dog), Primates (Humans, monkeys) belongs to class Mammalia.
6. Phylum – Similar classes put together in Phylum. Example Class-Pisces, Class- Amphibia, Class-Reptilia, and Class- Aves & Class-Mammalia included in Phylum Chordata. (Division for plants)
7. Kingdom – It is the largest taxon. All similar organisms put in one kingdom. Like – Plantae, Animalia.
| Taxon | Botany Suffix | Example | Zoology Suffix | Example |
| Kingdom | ||||
| Phylum/ Division | Phyta | Bryophyta | ||
| Class | Phyceae/ Opsida/ ae | Chlorophyceae / Brayopsida | ||
| Order | ales | Malvales | Iformes | Passeriformes |
| Family | aceae | Malvaceae | Idae | Hominidae |
| Genus | ||||
| Species |
Note – Tribe is subcategory between Family and Genus. The cohort is subcategory between Class and Order.
Taxonomical Hierarchy – In taxonomical hierarchy similarities in organisms decreases and differences increases
Two Kingdom Classifications
Carolus Linnaeus classified organisms in two kingdoms
- Plantae
- Animalia
Three Kingdom Classifications
Haeckel classified organisms in three kingdoms
- Protista
- Plantae
- Animalia
Four Kingdom Classifications
Copeland classified organisms in four kingdoms
- Monera (Mychota)
- Protista (Protoctista)
- Plantae (Metaphyta)
- (Metazoa)
Five Kingdom Classifications
It is mostly used. R.H. Whitaker classified organisms in four kingdoms
- Monera
- Protista
- Fungi
- Plantae
- Animalia
Six Kingdom Classifications
Carl Woose classified organisms in four kingdoms
- Archaebacteria
- Eubacteria
- Protista
- Fungi
- Plantae
- Animalia
Binomial Nomenclature
Specific names provide to organisms that contain two parts genus name & species names. Example Panthera leo for Lion.
Guidelines and Principles for Binomial Nomenclature:
a) scientific name should be in Latin or derived from Latin.
b) Scientific name contains two parts, the first word is Genus name; the second word is Species name.
Example Felis domestica for Cat.
Genus name – Felis
Species name – domestica
c) Name of genus starts with Capital letter while species name starts with a small letter.
d) It will be printed or typed in Italics and underlined when handwritten.
e) The name should be short (not more than 12 or less than 3 letters), precise & easy to pronounce.
f) Name of the author is written is an abbreviated form after the species name. Example- Mangifera indica Linn. (Linn for Linnaeus)
g) Name of genus and species should not be the same in the plant but can be the same in animals like Naja naja for cobra.
Example:
| Common Name | Scientific Name |
| Lotus | Nelumbo nucifera |
| Neem | Azadirachta indica |
| Mango | Mangifera indica |
| Lion | Panthera leo |
| Tiger | Panthera tigris |
| Leopard | Panthera pardus |
| Cat | Felis domestica |
| Peacock | Pavo cristatus |
| Human | Homo sapiens |
International agencies who provide rules for nomenclature
a) ICBN – International Code for Botanical Nomenclature
b) ICZN – International Code for Zoological Nomenclature
c) ICNB – International Code for Nomenclature of Bacteria
d) ICTV – International Committee for the Taxonomy of Viruses.
e) ICNCP – International Code for Nomenclature Cultivated Plants.
Taxonomical Aids
Taxonomical aids are the techniques and procedures used to store and preserve information of organisms or complete organisms as a spaceman.
Some important taxonomical aids are following –
- Herbarium – store dried plant on 11.5 x 16.5-inch paper sheet.
- Botanical garden- National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow. (NBRI), Indian Botanical Garden, Howrah, Kolkata. (IBG, Largest in India), Forest Research Institute, Dehradun (FRI), Royal Botanical Garden, Kew, (England- Largest in word)
- Museum
- Zoological parks – Kruger Zoological Park, South Africa – Largest in word
- Taxonomical Key – They analytical in nature and used to identify plants and animals.
- Monograph – Diagrammatic representation of any taxon.
- Manuals – Provide information about family, genus, and species of the particular area.
- Flora – List of plants and habitat & description of plants in a specific area
- Fauna – List of animals and habitat & description of animals in a specific area
Books wrote by Linnaeus
Systema Naturae
Genera Plantarum
Species Plantarum
Philosophia Botanica
For Hindi




